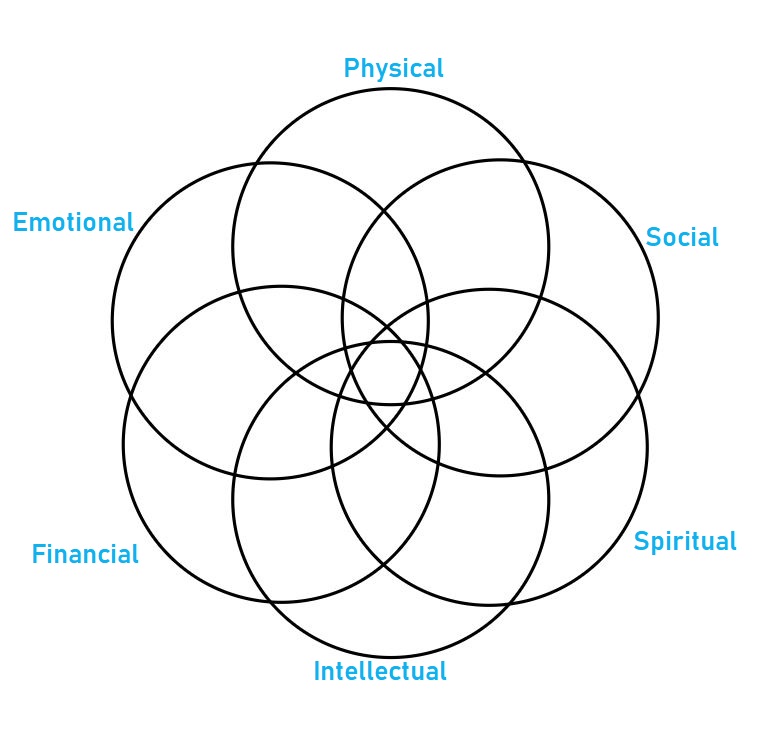
Police officers play a crucial role in maintaining public safety and upholding the law. Their profession demands resilience, adaptability, and a commitment to protecting and serving their communities. However, the intense and demanding nature of police work can take a toll on officers’ well-being in various ways. To more fully address officer well-being, the solution may be a multi-layered approach that emphasizes the interconnectedness of six areas of wellness—physical, emotional, intellectual, financial, social, and spiritual.
Physical Health
The physical demands placed on police officers are immense. From long hours of patrolling in a patrol vehicle to the need for quick and decisive action in critical situations, maintaining optimal physical fitness is paramount. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate rest are necessary to enhance officers’ physical well-being. Additionally, preventative measures and fitness programs may be able to reduce the risk of injuries and improve overall job performance.
The Importance of Regular Exercise
Physical fitness is the cornerstone of police officers’ ability to perform their duties effectively. Regular exercise not only helps individuals maintain a healthy weight but also enhances cardiovascular endurance, strength, and flexibility. These physical attributes are essential for officers who must respond rapidly to emergencies, pursue suspects, and handle physical altercations. Moreover, exercise contributes to stress reduction, increases mental well-being and resilience, and improves problem-solving abilities, all of which are vital for officers working in stressful environments.1
“The emotional toll of the job can lead to mental health challenges such as post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression. The significance of emotional resilience cannot be overstated, as officers face countless challenges that can impact their mental well-being”
Proper Nutrition for Optimal Performance
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting the physical and mental demands placed on police officers. A well-balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients to sustain energy levels, promote muscle recovery, and enhance cognitive function. Officers should prioritize a diet rich in lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to fuel their bodies adequately, but also keep hydrated. Proper nutrition improves physical performance, contributes to overall health, reduces the risk of chronic diseases and obesity, and promotes longevity in a profession that demands peak physical fitness.2
Adequate Rest for Recovery
Police officers often face irregular work schedules, long hours, and high-stress situations, making adequate rest essential for recovery. Quality sleep is crucial for physical and mental renewal, ensuring officers remain alert and focused during their duties. Sleep recharges the body and mind, and sleep deprivation can impair decision-making, reaction times, and overall job performance, posing serious risks to officers and the communities they serve. Prioritizing sufficient rest is fundamental for officers to maintain peak performance and resilience, as well as to reduce the likelihood of diseases and improve their body’s muscle repair.3
Preventative Measures and Fitness Programs
Preventative measures and fitness programs play an essential role in reducing the risk of injuries and overall health among police officers. Police agencies should invest in comprehensive fitness initiatives that address the specific physical demands of the job. These programs can include strength training, cardiovascular exercises, flexibility training, and injury prevention strategies. By implementing a program that focuses on officers’ physical fitness and resilience, these programs decrease the likelihood of injuries and contribute to improved job performance and job satisfaction.4
Emotional Health
Policing often exposes officers to traumatic events and high-stress situations. Emotional health is the ability to control emotions so that one feels comfortable expressing them appropriately. This includes self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. The emotional toll of the job can lead to mental health challenges such as post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression. The significance of emotional resilience cannot be overstated, as officers face countless challenges that can impact their mental well-being. The significance of emotional intelligence (EI), mental health support programs, and the stigma surrounding seeking help are also important to understand. A supportive and understanding work culture will foster emotional resilience among police officers.
Emotional Intelligence in Policing
EI encompasses the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions while effectively navigating interpersonal relationships. EI is crucial for officers to respond empathetically to diverse situations, de-escalate conflicts, and communicate effectively with the community. Officers with high EI can better handle the emotional toll of their profession, enhancing their overall well-being and job performance.
Mental Health Support Programs
Given the unique challenges police officers face, mental health support programs are vital for promoting emotional resilience. These programs should provide accessible and confidential ways for officers to seek assistance, such as counseling services, peer support, and mental health resources. Destigmatizing mental health support is paramount to encourage officers to proactively address any emotional challenges they may be experiencing, ultimately fostering a healthier and more resilient police force.
Stigma Surrounding Seeking Help
The stigma surrounding mental health within the policing community often deters officers from seeking the help they need. Fear of judgment, concerns about career repercussions, and a perceived lack of understanding have contributed to this stigma. Creating a culture that recognizes seeking help as a sign of strength rather than weakness is necessary. Leaders within police agencies must actively work to disable the cultural barriers preventing officers from accessing mental health support.
Strategies for Creating a Supportive Work Culture
Fostering emotional resilience among police officers requires a shift in organizational culture. Implementing strategies that prioritize mental health and emotional well-being can contribute to a more supportive work environment. These strategies may include
Education and Training: Providing officers with education and training on EI, stress management, and coping strategies equips them with the tools to navigate the challenges of their profession.
“The weight of financial concerns can contribute to anxiety, depression, and reduced job satisfaction. Financial stress may also lead to distractions on duty, affecting decision-making and reaction times.”
Peer Support Programs: Establishing peer support programs allows officers to connect with colleagues who may have experienced similar challenges. Peer support creates a safe space for open dialogue and shared experiences.
Leadership Advocacy: Leadership plays a pivotal role in setting the tone for the organizational culture. Leaders should actively advocate for mental health awareness, openly discuss their own experiences, and lead by example in seeking help when needed.
Confidential Counseling Services: Ensuring access to confidential counseling services demonstrates an organizational commitment to supporting officers’ mental health without fear of judgment or reprisal.
Intellectual Health
Intellectual health means “perception” or “understanding.” It is the highest thinking power and involves rational, logical, and critical thinking. The landscape of policing is dynamic and ever evolving, presenting officers with an array of complex challenges. Continuous learning and intellectual stimulation are crucial for the development and effectiveness of police officers. Ongoing training, education, and skill development are critical for intellectual health. Fostering a culture of curiosity and critical thinking within police agencies can help to ensure officers are well-equipped to handle the complexities of modern policing.
Ongoing Training and Skill Development
Police officers face a plethora of scenarios, from routine duties to high-stakes situations that require split-second decision-making. Ongoing training and skill development are imperative to keep officers up to date on the latest techniques, technologies, and legal updates. Specialized training in areas such as de-escalation tactics, cultural sensitivity, and crisis intervention provides officers with the tools needed to navigate complex situations responsibly and effectively. Regular skill development not only enhances officers’ capabilities, but it also encourages confidence and adaptability, key strengths in meeting the challenges of policing.
Education as a Foundation
A vigorous educational foundation is crucial for officers to comprehend the legal, ethical, and societal aspects of their roles. Academic programs, workshops, and seminars provide opportunities for officers to deepen their knowledge of criminal justice principles, constitutional rights, and evolving legal standards. Education solidifies the groundwork for critical thinking, enabling officers to comprehensively analyze situations and make informed decisions.
Fostering a Culture of Curiosity
Cultivating a culture of curiosity within police agencies involves encouraging officers to ask questions, seek knowledge, and explore new perspectives. This curiosity-driven approach extends beyond mandatory training, creating an environment where officers are motivated to stay informed and engaged in their profession. Whether officers are exploring new policing strategies, technology advancements, or developments in community engagement, a culture of curiosity creates continuous improvement and a forward-thinking mindset.
Critical Thinking in Policing
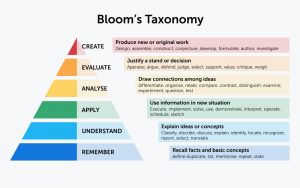
Critical thinking is the cornerstone of effective decision-making, especially in the dynamic and high-stakes environment of policing. Officers must analyze situations, consider other perspectives, and make judgment calls. Emphasizing critical thinking skills in training and education empowers officers to navigate ambiguity, assess the legitimacy of information, and respond to challenges with adaptability and reason. A critical thinking culture encourages officers to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, and apply ethical principles in their decision-making processes. Bloom’s Taxonomy examines the development of intellectual skills. The simplest behavior is at the base and the skills progress upward to more complex behaviors. The first level must be mastered before the next can take place.
Practical Benefits
Enhanced Problem-Solving: Ongoing training empowers officers with the skills needed to approach complex problems with creativity and efficacy.
Improved Communication: A well-informed and critically thinking workforce enhances communication skills, allowing officers to engage effectively with the community, stakeholders, and other police personnel.
Adaptability to Change: Continuous learning fosters adaptability, ensuring that officers are equipped to confidently navigate challenges in a quickly changing environment.
Increased Professionalism: A commitment to ongoing education instills a sense of professionalism among officers, elevating the standards of the entire police community.
Financial Health
Financial stability is a cornerstone of overall well-being, as financial problems can directly relate to stress and can cause fights and divorce in a marriage. Police officers are not immune to the challenges associated with managing their finances. Police professionals have unique financial considerations, including pension/retirement planning, budgeting, and financial literacy. Financial stress plays a role in mental health and job performance, but there are ways to achieve financial wellness.
Financial Considerations for Law Enforcement Professionals
Pension Planning: The stability of a pension plan plays a pivotal role in the financial well-being of police professionals. Agencies and officers must work together to understand and maximize pension benefits. Officers should stay informed about their pension plan details, retirement eligibility, and any supplemental retirement savings options available to them. Early and strategic pension planning is essential for a secure financial future.
Budgeting: Establishing and adhering to a comprehensive budget is crucial for managing financial resources effectively. Police professionals need to consider their income, expenses, and savings goals. Budgeting allows officers to allocate funds for essentials, plan for future expenses, and build a financial safety net. Regularly reviewing and adjusting budgets ensures that financial goals remain realistic and achievable.
“Fostering a supportive and inclusive social environment is essential for success in both the personal and professional realms.”
Financial Literacy: Enhancing financial literacy is an ongoing process that empowers police professionals to make informed decisions about their money. Financial literacy education should cover topics such as investment strategies, debt management, and understanding financial products. Agencies can facilitate workshops or provide resources to improve officers’ financial knowledge, enabling them to navigate the complexities of personal finance with confidence.5
The Impact of Financial Stress on Mental Health and Job Performance
Financial stress can have a profound impact on mental health and job performance. The weight of financial concerns can contribute to anxiety, depression, and reduced job satisfaction. Financial stress may also lead to distractions on duty, affecting decision-making and reaction times. Recognizing the interconnectedness of financial well-being and mental health is crucial for creating a supportive environment within police agencies.
Practical Tips for Achieving Financial Wellness
Seek Financial Counseling: Police agencies can offer access to financial counseling services, providing officers with personalized guidance on budgeting, debt management, and long-term financial planning.
“Creating surroundings where police officers feel comfortable searching out assistance and overtly discussing their stories contributes to the overall well-being of the police network”
Create Emergency Funds: Encourage officers to build emergency funds to cover unforeseen expenses. Having a financial safety net reduces stress and allows individuals to navigate unexpected challenges without compromising their financial stability.
Invest Wisely: Provide education on investment options and strategies to help officers make informed decisions about their retirement savings. Understanding the long-term benefits of solid investment practices is essential for achieving financial security.
Promote Financial Education Programs: Agencies and police academies can host workshops, seminars, or online resources to promote financial literacy among police professionals. Covering topics such as credit management, savings, and retirement planning can empower officers to make appropriate financial decisions.
Social Health
The ability to interact well with the community and colleagues and to have satisfying interpersonal relationships is at the forefront of policing. However, this ability is dependent on having satisfying and enriching relationships. In the ever-evolving landscape of policing, the significance of effective communication, teamwork, and community engagement cannot be overstated. Police officers play a vital role in maintaining public safety. Fostering a supportive and inclusive social environment is essential for success in both the personal and professional realms.
Effective Communication
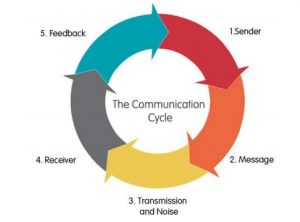
Effective communication lies at the heart of successful policing. Police officers must communicate clearly and efficiently with colleagues, superiors, and the community to ensure the smooth execution of their duties. Communication is two-directional. The sender transmits a message to the receiver. Once the receiver processes the message by listening, they provide feedback to the sender. The message sent must be clear and without ambiguity.
Proper communication fosters a sense of unity within police agencies, enhances team collaboration, and ultimately leads to more effective crime prevention and resolution. Furthermore, open lines of communication between officers and the community build trust, encouraging cooperation and partnership in the pursuit of public safety. Communication also has nonverbal components; therefore, police officers should be mindful of tone, posture, and verbiage.
Teamwork
Policing is fundamentally a team-oriented profession, and the ability to work flawlessly as part of a team is vital for officers’ success. A strong team dynamic promotes trust, camaraderie, and mutual support, contributing to improved morale and job satisfaction. Effective teamwork enables officers to share expertise, collect resources, and respond more efficiently to critical events. By fostering a culture that values and prioritizes teamwork, police agencies can create a resilient and cohesive force capable of navigating the complexities of modern policing.
Community Engagement
Building positive relationships with the community is a cornerstone of effective policing. Community engagement goes beyond enforcing the law; it involves understanding and addressing the unique needs and concerns of the people officers serve. Regular interactions, outreach programs, and community policing initiatives strengthen the bond between officers and the public, creating an environment of collaboration. Engaging with the community fosters a sense of shared responsibility for public safety, empowering both officers and community members to work together toward common goals. Police officers can show empathy and compassion, examining the situation from all angles. This helps build trust and rapport with others as well as bringing positivity and healing to a traumatic situation.
Strategies for Fostering a Supportive and Inclusive Social Environment
Diversity and Inclusion Training: Implementing comprehensive diversity and inclusion training programs ensures that officers are equipped with the knowledge and skills to navigate diverse communities respectfully. This fosters a more inclusive social environment within police agencies.
Community Policing Initiatives: Actively engaging in community policing initiatives allows officers to build positive relationships with community members. Regular meetings, events, and outreach programs contribute to creating a supportive social environment where trust and cooperation thrive.
“Building a supportive community within police agencies encourages officers to share experiences, seek guidance, and offer support”
Peer Support Programs: Establishing peer support programs within police agencies provides officers with a network of colleagues who understand the unique challenges of the profession. This creates a supportive social environment where officers can openly discuss concerns and seek assistance when needed.
Transparent Communication Channels: Ensuring transparent communication channels between police agencies and the community builds trust. Regular town hall meetings, public forums, and online platforms facilitate open dialogue, enabling officers to address community concerns and vice versa.
Addressing Social Challenges
Recognizing and addressing the socially demanding situations faced by police officers is crucial for cultivating high-quality social surroundings. This includes imparting mental health resources; promoting a healthy and stable work-life balance; and presenting a guide for officers handling stress, trauma, or burnout. Creating surroundings where police officers feel comfortable searching out assistance and overtly discussing their stories contributes to the overall well-being of the police network.
Spiritual Health
Spiritual well-being is often overlooked but plays a significant role in the holistic health of police officers. The spiritual dimension of police officer wellness is gaining recognition. Police officers can explore the importance of finding meaning and purpose in one’s work, developing resilience through spiritual practices, and fostering a sense of connection and community. A holistic approach to police officer wellness encompasses officers’ spiritual well-being and its impact on mental health, job satisfaction, and overall life satisfaction.
Finding Meaning and Purpose in Work
Finding meaning and purpose in one’s work is a fundamental aspect of overall well-being, particularly for those in high-stakes professions like policing. Police officers who perceive their work as meaningful are more likely to be engaged, motivated, and resilient in the face of challenges. Recognizing the impact of their service on the community and society at large allows officers to develop a sense of purpose that goes beyond daily tasks.
Developing Resilience Through Spiritual Practices
Resilience is a key factor in coping with the stressors inherent in police work. Spiritual practices, which can encompass a wide range of beliefs and activities, provide a framework for officers to develop resilience and cope with adversity. Whether through prayer, meditation, mindfulness, or other forms of spiritual engagement, officers can find solace, strength, and perspective. Spiritual practices contribute to emotional regulation, stress reduction, and the ability to maintain focus and composure in challenging situations, thus fostering a resilient mindset.
Fostering a Sense of Connection and Community
A sense of connection and community is essential for police officers, who often face unique challenges that only their peers can truly understand. Building a supportive community within police agencies encourages officers to share experiences, seek guidance, and offer support. This camaraderie not only enhances professional relationships, but also contributes to a sense of belonging and connection.
Strategies for Supporting Spiritual Wellness
A holistic approach to police officer wellness acknowledges the importance of the spiritual dimension alongside physical and mental well-being. Agencies can support officers by
Incorporating Spiritual Wellness Programs: Providing resources and opportunities for officers to explore and engage in spiritual practices can be integrated into wellness programs.
Promoting Peer Support: Encouraging officers to share their experiences and provide support to one another fosters a sense of community and connection.
Teaching Holistic Wellness: Agencies can offer training and education on the importance of holistic wellness, emphasizing the role of spirituality in overall well-being.
The Impact of Spiritual Well-Being
Finding meaning, belonging, and inner calm are important for police officers’ well-being. How police officers see their place in the world and connect with others affects mental health, work fulfillment, and happiness in life. Police officers who feel these deeper meanings are less likely to feel stressed, worried, or burnt out. They may feel more rewarded and more satisfied knowing they helped people.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the well-being of police officers is a multifaceted and interconnected tapestry that encompasses physical, emotional, intellectual, financial, social, and spiritual dimensions. These are not the only dimensions that affect police officers. Other areas of health may include environmental, occupational, cultural, and digital wellness. Recognizing and addressing the diverse aspects of officers’ health is essential for creating a resilient, effective, and fulfilled policing community. Implementing comprehensive support systems that prioritize all dimensions if wellness ensures that police officers who dedicate their lives to protecting and serving their communities are equipped to navigate the challenges of their profession while maintaining optimal health and well-being. d
Notes:
1IACP, Health and Fitness: Importance to Law Enforcement Officers, Training Key 685, 2018.
2IACP, Nutritional Needs, Supporting Officer Safety Through Family Wellness (2018); IACP, Eating Well on the Go (Bureau of Justice Services, 2022); IACP, Exercise and Nutrition, Training Key 690.
3 IACP, The Effects of Sleep Deprivation, Supporting Officer Safety Through Family Wellness”; IACP, Exercise and Nutrition.
4IACP, Fitness Program Development Considerations (2018).
5IACP, Financial Literacy, Supporting Officer Safety Through Family Wellness (2018).
Please cite as
Jennifer Wessels, and Ronald Davis, “The Six Facets of Holistic Wellness,” Police Chief Online, December 18, 2024.



